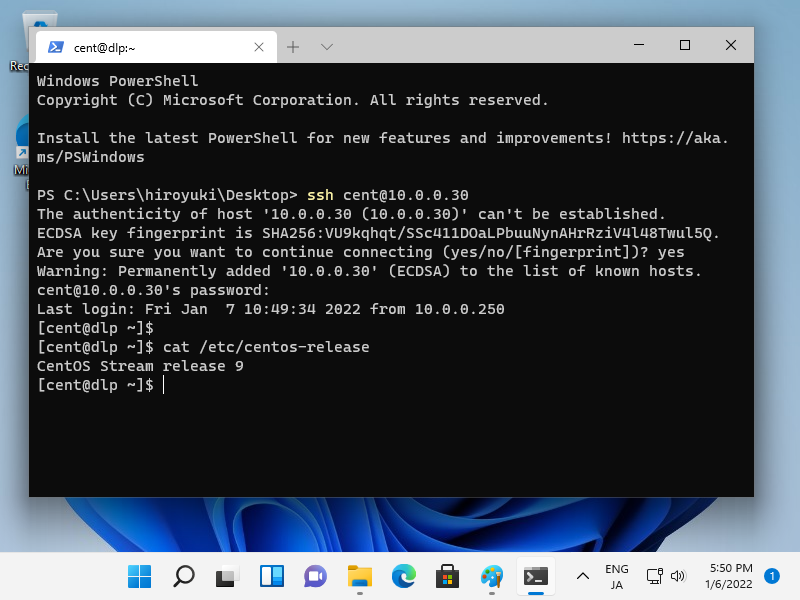
¶ OpenSSH: Password Authentication
Configure SSH Server to operate servers from remote computers.
¶ OpenSSH Default Installation
-
OpenSSH Default Setup:
OpenSSH is already installed by default with CentOS Stream, even with a Minimal Install. -
Password Authentication:
By default, you can log in with password authentication. For improved security, it's advisable to change thePermitRootLoginparameter.vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config # line 40: change (prohibit root login) # Options: [prohibit-password], [forced-commands-only] PermitRootLogin no systemctl restart sshd -
Firewall Settings for SSH:
If Firewalld is running, allow SSH service. SSH uses22/TCP.firewall-cmd --add-service=ssh firewall-cmd --runtime-to-permanentThe command should return
successupon completion.
¶ SSH Client Configuration: CentOS
-
Install SSH Client:
dnf -y install openssh-clients -
Connect to SSH Server:
Connect using a common user.ssh username@(hostname or IP address)Example:
ssh cent@dlp.emc.world -
Executing Remote Commands:
You can execute commands on the remote host via SSH.ssh username@hostname "command"Example:
ssh cent@dlp.emc.world "cat /etc/passwd"
¶ SSH Client Configuration: Windows #1
-
Download a SSH Client:
For Windows, download and install a SSH client like PuTTY. -
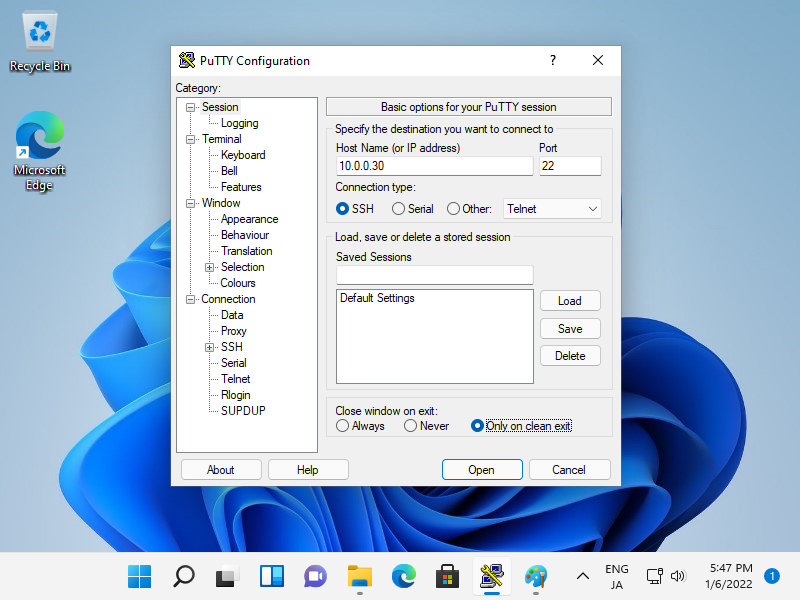
Connecting with PuTTY:
Start PuTTY, input your server's hostname or IP address, and click [Open] to connect.
-
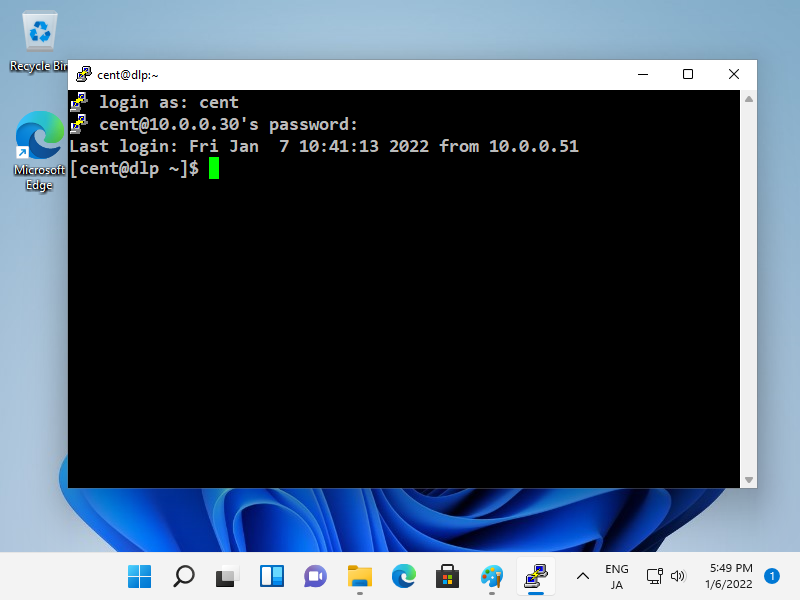
After successing authentication, it's possible to login and operate CentOS server from remote computer
¶ SSH Client Configuration: Windows #2
- Using OpenSSH in Windows 11:
In Windows 11, OpenSSH Client is implemented as a Windows feature. You can use thesshcommand in PowerShell or Command Prompt without third-party software like PuTTY.